Stefaan Verhulst
Paper by Veeckman, Carina and van der Graaf, Shenja: “Nowadays the smart-city concept is shifting from a top-down, mere technological approach towards bottom-up processes that are based on the participation of creative citizens, research organisations and companies. Here, the city acts as an urban innovation ecosystem in which smart applications, open government data and new modes of participation are fostering innovation in the city. However, detailed analyses on how to manage smart city initiatives as well as descriptions of underlying challenges and barriers seem still scarce. Therefore, this paper investigates four, collaborative smart city initiatives in Europe to learn how cities can optimize the citizen’s involvement in the context of open innovation. The analytical framework focuses on the innovation ecosystem and the civic capacities to engage in the public domain. Findings show that public service delivery can be co-designed between the city and citizens, if different toolkits aligned with the specific capacities and skills of the users are provided. By providing the right tools, even ordinary citizens can take a much more active role in the evolution of their cities and generate solutions from which both the city and everyday urban life can possibly benefit.”
New book by Nathan Eagle and Kate Greene : “Big Data is made up of lots of little data: numbers entered into cell phones, addresses entered into GPS devices, visits to websites, online purchases, ATM transactions, and any other activity that leaves a digital trail. Although the abuse of Big Data—surveillance, spying, hacking—has made headlines, it shouldn’t overshadow the abundant positive applications of Big Data. In Reality Mining, Nathan Eagle and Kate Greene cut through the hype and the headlines to explore the positive potential of Big Data, showing the ways in which the analysis of Big Data (“Reality Mining”) can be used to improve human systems as varied as political polling and disease tracking, while considering user privacy.
Quentin Hardy in the New York Times: “New technology products head at us constantly. There’s the latest smartphone, the shiny new app, the hot social network, even the smarter thermostat.
As great (or not) as all these may be, each thing is a small part of a much bigger process that’s rarely admired. They all belong inside a world-changing ecosystem of digital hardware and software, spreading into every area of our lives.
Thinking about what is going on behind the scenes is easier if we consider the automobile, also known as “the machine that changed the world.” Cars succeeded through the widespread construction of highways and gas stations. Those things created a global supply chain of steel plants and refineries. Seemingly unrelated things, including suburbs, fast food and drive-time talk radio, arose in the success.
Today’s dominant industrial ecosystem is relentlessly acquiring and processing digital information. It demands newer and better ways of collecting, shipping, and processing data, much the way cars needed better road building. And it’s spinning out its own unseen businesses.
A few recent developments illustrate the new ecosystem. General Electric plans to announce Monday that it has created a “data lake” method of analyzing sensor information from industrial machinery in places like railroads, airlines, hospitals and utilities. G.E. has been putting sensors on everything it can for a couple of years, and now it is out to read all that information quickly.
The company, working with an outfit called Pivotal, said that in the last three months it has looked at information from 3.4 million miles of flights by 24 airlines using G.E. jet engines. G.E. said it figured out things like possible defects 2,000 times as fast as it could before.
The company has to, since it’s getting so much more data. “In 10 years, 17 billion pieces of equipment will have sensors,” said William Ruh, vice president of G.E. software. “We’re only one-tenth of the way there.”
It hardly matters if Mr. Ruh is off by five billion or so. Billions of humans are already augmenting that number with their own packages of sensors, called smartphones, fitness bands and wearable computers. Almost all of that will get uploaded someplace too.
Shipping that data creates challenges. In June, researchers at the University of California, San Diego announced a method of engineering fiber optic cable that could make digital networks run 10 times faster. The idea is to get more parts of the system working closer to the speed of light, without involving the “slow” processing of electronic semiconductors.
“We’re going from millions of personal computers and billions of smartphones to tens of billions of devices, with and without people, and that is the early phase of all this,” said Larry Smarr, drector of the California Institute for Telecommunications and Information Technology, located inside U.C.S.D. “A gigabit a second was fast in commercial networks, now we’re at 100 gigabits a second. A terabit a second will come and go. A petabit a second will come and go.”
In other words, Mr. Smarr thinks commercial networks will eventually be 10,000 times as fast as today’s best systems. “It will have to grow, if we’re going to continue what has become our primary basis of wealth creation,” he said.
Add computation to collection and transport. Last month, U.C. Berkeley’s AMP Lab, created two years ago for research into new kinds of large-scale computing, spun out a company called Databricks, that uses new kinds of software for fast data analysis on a rental basis. Databricks plugs into the one million-plus computer servers inside the global system of Amazon Web Services, and will soon work inside similar-size megacomputing systems from Google and Microsoft.
It was the second company out of the AMP Lab this year. The first, called Mesosphere, enables a kind of pooling of computing services, building the efficiency of even million-computer systems….”
Luke Fretwell at GovFresh: “Earlier this year, I began doing research work with CivicActions on agile development in government — who was doing it, how and what the needs were to successfully get it deployed.
After the Healthcare.gov launch mishaps, calls for agile practices as the panacea to all of government IT woes reached a high. While agile as the ultimate solution oversimplifies the issue, we’ve evolved as a profession (both software development and public service) that moving towards an iterative approach to operations is the way of the future.
My own formal introduction with agile began with my work with CivicActions, so the research coincided with an introductory immersion into how government is using it. Having been involved with startups for the past 15 years, iterative development is the norm, however, the layer of project management processes has forced me to be a better professional overall.
What I’ve found through many discussions and interviews is that you can’t just snap your fingers and execute agile within the framework of government bureaucracy. There are a number of issues — from procurement to project management training to executive-level commitment to organizational-wide culture change — that hinder its adoption. For IT, launching a new website or app is this easy part. Changing IT operational processes and culture is often overlooked or avoided, especially for a short-term executive, because they reach into the granular organizational challenges most people don’t want to bother with.
After talking with a number of agile government and private sector practitioners, it was clear there was enthusiasm around how it could be applied to fundamentally change the way government works. Beyond just execution from professional project management professionals, everyone I spoke with talked about how deploying agile gives them a stronger sense of public service.
What came from these discussions is the desire to have a stronger community of practitioners and those interested in deploying it to better support one another.
To meet that need, a group of federal, state, local government and private sector professionals have formed Agile for Gov, a “community-powered network of agile government professionals.”…
Chris Holden and Maynard Holliday at Commons Lab: “Traditional monitoring of arms control treaties, agreements, and commitments has required the use of National Technical Means (NTM)—large satellites, phased array radars, and other technological solutions. NTM was a good solution when the treaties focused on large items for observation, such as missile silos or nuclear test facilities. As the targets of interest have shrunk by orders of magnitude, the need for other, more ubiquitous, sensor capabilities has increased. The rise in web-based, or cloud-based, analytic capabilities will have a significant influence on the future of arms control monitoring and the role of citizen involvement.
Since 1999, the U.S. Department of State has had at its disposal the Key Verification Assets Fund (V Fund), which was established by Congress. The Fund helps preserve critical verification assets and promotes the development of new technologies that support the verification of and compliance with arms control, nonproliferation, and disarmament requirements.
Sponsored by the V Fund to advance web-based analytic capabilities, Sandia National Laboratories, in collaboration with Recorded Future (RF), synthesized open-source data streams from a wide variety of traditional and nontraditional web sources in multiple languages along with topical texts and articles on national security policy to determine the efficacy of monitoring chemical and biological arms control agreements and compliance. The team used novel technology involving linguistic algorithms to extract temporal signals from unstructured text and organize that unstructured text into a multidimensional structure for analysis. In doing so, the algorithm identifies the underlying associations between entities and events across documents and sources over time. Using this capability, the team analyzed several events that could serve as analogs to treaty noncompliance, technical breakout, or an intentional attack. These events included the H7N9 bird flu outbreak in China, the Shanghai pig die-off and the fungal meningitis outbreak in the United States last year.
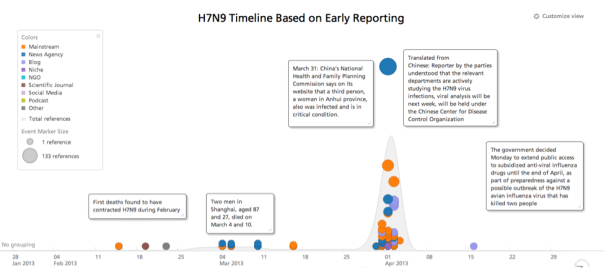
For H7N9 we found that open source social media were the first to report the outbreak and give ongoing updates. The Sandia RF system was able to roughly estimate lethality based on temporal hospitalization and fatality reporting. For the Shanghai pig die-off the analysis tracked the rapid assessment by Chinese authorities that H7N9 was not the cause of the pig die-off as had been originally speculated. Open source reporting highlighted a reduced market for pork in China due to the very public dead pig display in Shanghai. Possible downstream health effects were predicted (e.g., contaminated water supply and other overall food ecosystem concerns). In addition, legitimate U.S. food security concerns were raised based on the Chinese purchase of the largest U.S. pork producer (Smithfield) because of a fear of potential import of tainted pork into the United States….
To read the full paper, please click here.”
EU Press Release: “Every single minute, the world generates 1.7 million billion bytes of data, equal to 360,000 DVDs. How can our brain deal with increasingly big and complex datasets? EU researchers are developing an interactive system which not only presents data the way you like it, but also changes the presentation constantly in order to prevent brain overload. The project could enable students to study more efficiently or journalists to cross check sources more quickly. Several museums in Germany, the Netherlands, the UK and the United States have already showed interest in the new technology.
Data is everywhere: it can either be created by people or generated by machines, such as sensors gathering climate information, satellite imagery, digital pictures and videos, purchase transaction records, GPS signals, etc. This information is a real gold mine. But it is also challenging: today’s datasets are so huge and complex to process that they require new ideas, tools and infrastructures.
Researchers within CEEDs (@ceedsproject) are transposing big data into an interactive environment to allow the human mind to generate new ideas more efficiently. They have built what they are calling an eXperience Induction Machine (XIM) that uses virtual reality to enable a user to ‘step inside’ large datasets. This immersive multi-modal environment – located at Pompeu Fabra University in Barcelona – also contains a panoply of sensors which allows the system to present the information in the right way to the user, constantly tailored according to their reactions as they examine the data. These reactions – such as gestures, eye movements or heart rate – are monitored by the system and used to adapt the way in which the data is presented.
Jonathan Freeman,Professor of Psychology at Goldsmiths, University of London and coordinator of CEEDs, explains: “The system acknowledges when participants are getting fatigued or overloaded with information. And it adapts accordingly. It either simplifies the visualisations so as to reduce the cognitive load, thus keeping the user less stressed and more able to focus. Or it will guide the person to areas of the data representation that are not as heavy in information.”
Neuroscientists were the first group the CEEDs researchers tried their machine on (BrainX3). It took the typically huge datasets generated in this scientific discipline and animated them with visual and sound displays. By providing subliminal clues, such as flashing arrows, the machine guided the neuroscientists to areas of the data that were potentially more interesting to each person. First pilots have already demonstrated the power of this approach in gaining new insights into the organisation of the brain….”
Joshua Chambers at FutureGov: “Governments across the region are turning to “gamification” – otherwise known as “game science” – to help create new ways to persuade their populations.
FutureGov recently attended a session at GovCamp Australia where officials discussed the potential of this new approach. It has pulled together the best examples of successful government games, and sought advice from the private sector on building something that will achieve results.
How it works
How does gamification work? It creates an environment where people play games to win prizes or compete against one another, all while learning about about a new message or behaving in a certain, desirable manner. The approach can be used by every type of agency, and has been trialled on public sector campaigns including military recruitment, physical fitness, speeding prevention, consumer rights awareness and even making citizens engage with census data.
For example, it was used by the Department of Justice of Victoria, Australia when they wanted to make young people aware of consumer protection laws. Discussion of legal concepts did not seem particularly appealing, so they took a different tack by launching a game called Party for Your Rights. “It’s targeted at young people, teaching them their rights through the activity of going to a party. It’s very appealing, with retro 1980s graphics and music,” explained Paul Chandley, general manager of digital strategy and engagement in the Victorian Department of Justice.
Since its launch in June 2014, it has been played 23,000 times. A survey found that 96% of players surveyed said they felt either more informed of their rights or more confident about using their rights after interacting with the game.
The game proved popular in Australia and there are plenty of other examples of successful games built by government agencies – FutureGov has profiled the six best examples of gamification in government.…”
See also:
at Quartz: “This week African leaders met with officials in Washington and agreed to billions of dollars of US investments and infrastructure deals. But the terrible state of statistical reporting in most of Africa means that it will be nearly impossible to gauge how effective these deals are at making Africans, or the American investors, better off.
Data reporting on the continent is sketchy. Just look at the recent GDP revisions of large countries. How is it that Nigeria’s April GDP recalculation catapulted it ahead of South Africa, making it the largest economy in Africa overnight? Or that Kenya’s economy is actually 20% larger (paywall) than previously thought?
Indeed, countries in Africa get noticeably bad scores on the World Bank’s Bulletin Board on Statistical Capacity, an index of data reporting integrity.
A recent working paper from the Center for Global Development (CGD) shows how politics influence the statistics released by many African countries…
But in the long run, dodgy statistics aren’t good for anyone. They “distort the way we understand the opportunities that are available,” says Amanda Glassman, one of the CGD report’s authors. US firms have pledged $14 billion in trade deals at the summit in Washington. No doubt they would like to know whether high school enrollment promises to create a more educated workforce in a given country, or whether its people have been immunized for viruses.
Overly optimistic indicators also distort how a government decides where to focus its efforts. If school enrollment appears to be high, why implement programs intended to increase it?
The CGD report suggests increased funding to national statistical agencies, and making sure that they are wholly independent from their governments. President Obama is talking up $7 billion into African agriculture. But unless cash and attention are given to improving statistical integrity, he may never know whether that investment has borne fruit”
Lorenzo Franceschi-Bicchierai at Mashable: “For more than three years, Syria has been crippled by a bloody civil war that has laid waste to cities and exacted a heavy civilian toll. But because reporting in Syria is so dangerous, the bloodletting has largely taken place away from the media spotlight. One group of researchers, though, is determined to document every single killing.
Through painstaking data-gathering and assiduous verification, the group Syrian Tracker has tallied 111,915 deaths in the course of the conflict so far.
Syria Tracker gets reports from eyewitnesses and volunteers on the ground. Researchers also cull data from news reports.
The database has yielded some important insights such as possible war crimes committed by the Syrian regime.
Working in collaboration with researchers from the nonprofit organization SumAll.org, the researchers discovered that more women were getting killed in the conflict. In April of 2011, women made up only 1% of those killed. Today, 13% of victims are women, according to the latest data.
Those numbers alone don’t tell the whole story, though. Taking a closer look at how women were killed, the researchers discovered a pattern. Women weren’t random victims of bombings for example. Instead, many were killed by snipers, indicating a deliberate policy to go after female civilians, which would constitute a war crime.
Data on how children were killed suggest a similar conclusions. Of the thousands killed in the conflict, at least 700 have been summarily executed and tortured, and about 200 boys under the age of 13 have been killed by sniper fire, according to the data…”
Liz Stinson in Wired: “…Last week in the journal Science, the researchers (led by University of Texas art historian Maximilian Schich) published a study that looked at the cultural history of Europe and North America by mapping the birth and deaths of more than 150,000 notable figures—including everyone from Leonardo Da Vinci to Ernest Hemingway. That data was turned into an amazing animated infographic that looks strikingly similar to the illustrated flight paths you find in the back of your inflight magazine. Blue dots indicate a birth, red ones means death.
The researchers used data from Freebase, which touts itself as a “community curated database of people, places and things.” This gives the data a strong western-bent. You’ll notice that many parts of Asia and the Middle East (not to mention pre-colonized North America), are almost wholly ignored in this video. But to be fair, the abstract did acknowledge that the study was focused mainly on Europe and North America.
Still, mapping the geography of cultural migration does gives you some insight about how the kind of culture we value has shifted over the centuries. It’s also a novel lens through which to view our more general history, as those migration trends likely illuminate bigger historical happenings like wars and the building of cross-country infrastructure.
