Stefaan Verhulst
Conference Paper by Bettina Schorr: “Due to high social inequalities and weak public institutions, political corruption and the influence of business elites on policy-makers are widespread in the Andean region. The consequences for the opportunities of sustainable development are serious: regulation limiting harmful business activities or (re-)distributive reforms are difficult to achieve and public resources often end up as private gains instead of serving development purposes.
Given international and domestic pressures, political corruption has reached the top of the political agendas in many countries. However, frequently transparency goals do not materialize into new binding policies or, when reforms are enacted, they suffer from severe implementation gaps.
The paper analyses transparency politics in Chile where a series of reforms regarding political transparency were implemented since 2014. Hence, Chile counts among the few successful cases in the region. By tracing the process that led to the emergence of new transparency policies in Chile, the paper elaborates an analytical framework for the explanation of institutional innovation in the case of political transparency. In particular, the study emphasizes the importance of civil society actors´ involvement in the whole policy cycle, particularly in the stages of formulation, implementation and evaluation….(More)”.
Jasmin Gray at Huffington Post: “The NHS has pulled out of a controversial data-sharing arrangement with the Home Office which saw confidential patients’ details passed on to immigration enforcers.
In May, the government suspended the ‘memorandum of understanding’ agreement between the health service and the Home Office after MPs, doctors and health charities warned it was leaving seriously ill migrants too afraid to seek medical treatment.
But on Tuesday, NHS Digital announced that it was cutting itself out of the agreement altogether.
“NHS Digital has received a revised narrowed request from the Home Office and is discussing this request with them,” a spokesperson for the data-branch of the health service said, adding that they have “formally closed-out our participation” in the previous memorandum of understanding.
The anxieties of “multiple stakeholder communities” to ensure the agreement made by the government was respected was taken into account in the decision, they added.
Meanwhile, the Home Office confirmed it was working to agree a new deal with NHS Digital which would only allow it to make requests for data about migrants “facing deportation action because they have committed serious crimes, or where information necessary to protect someone’s welfare”.
The move has been welcomed by campaigners, with Migrants’ Rights Network director Rita Chadra saying that many migrants had missed out on “the right to privacy and access to healthcare” because of the data-sharing mechanism
Paper by David Rozas et all: “Blockchain technologies have generated excitement, yet their potential to enable new forms of
We approach blockchain through the identification and
MIT Technology Review: “Weather forecasting is impressively accurate given how changeable and chaotic Earth’s climate can be. It’s not unusual to get 10-day forecasts with a reasonable level of accuracy.
But there is still much to be done. One challenge for meteorologists is to improve their “nowcasting,” the ability to forecast weather in the next six hours or so at a spatial resolution of a square kilometer or less.
In areas where the weather can change rapidly, that is difficult. And there is much at stake. Agricultural activity is increasingly dependent on nowcasting, and the safety of many sporting events depends on it too. Then there is the risk that sudden rainfall could lead to flash flooding, a growing problem in many areas because of climate change and urbanization. That has implications for infrastructure, such as sewage management, and for safety, since this kind of flooding can kill.
So meteorologists would dearly love to have a better way to make their nowcasts.
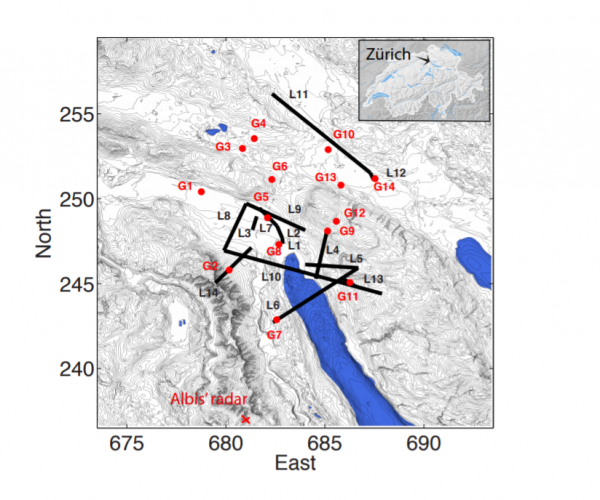
Enter Blandine Bianchi from EPFL in Lausanne, Switzerland, and a few colleagues, who have developed a method for combining meteorological data from several sources to produce nowcasts with improved accuracy. Their work has the potential to change the utility of this kind of forecasting for everyone from farmers and gardeners to emergency services and sewage engineers.
Current forecasting is limited by the data and the scale on which it is gathered and processed. For example, satellite data has a spatial resolution of 50 to 100 km and allows the tracking and forecasting of large cloud cells over a time scale of six to nine hours. By contrast, radar data is updated every five minutes, with a spatial resolution of about a kilometer, and leads to predictions on the time scale of one to three hours. Another source of data is the microwave links used by telecommunications companies, which are degraded by rainfall….(More)”
Michael Krumholtz at LATAM Tech: “Unfortunately, in Latin America and many other places around the world, robberies are a part of urban life. Moisés Salazar of Lima has been a victim of petty crime in the streets, which is what led him to create Reach.
The application that markets itself as a kind of Waze for street crime alerts users through a map of incident reports or crimes that display visibly on your phone….
Salazar said that Reach helps users before, during and after incidents that could victimize them. That’s because the map allows users to avoid certain areas where a crime may have just happened or is being carried out.
In addition, there is a panic button that users can push if they find themselves in danger or in need of authorities. After the fact, that data then gets made public and can be analyzed by expert users or authorities wanting to see which incidents occur most commonly and where they occur.
Reach is very similar to the U.S. application Citizen, which is a crime avoidance tool used in major metropolitan areas in the U.S. like New York. That application alerts users to crime reports in their neighborhoods and gives them a forum to either record anything they witness or talk about it with other users….(More)”.
Paper by Henry Farrell and Abraham L. Newman: “…Domestically, policy-makers and scholars argued that information openness, like economic openness, would go hand-in-glove with political liberalization and the spread of democratic values. This was perhaps, in part an accident of timing: the Internet – which seemed to many to be inherently resistant to censorship – burgeoned shortly after the collapse of Communism in the Soviet Union and Eastern Europe. Politicians celebrated the dawn of a new era of open communication, while scholars began to argue that the spread of the Internet would lead to the spread of democracy (Diamond 2010;Shirky 2008).
A second wave of literature suggested that Internet-based social media had played a crucial role in spreading freedom in the Arab Spring (Howard 2010; Hussain and Howard 2013). There were some skeptics who highlighted the vexed relationship between open networks and the closed national politics of autocracies (Goldsmith and Wu 2006), or who pointed out that the Internet was nowhere near as censorship-resistant as early optimists had supposed (Deibert et al. 2008). Even these pessimists seemed to believe that the Internet could bolster liberalism in healthy democracies, although it would by no means necessarily prevail over tyranny.
The international liberal order for information, however, finds itself increasingly on shaky ground. Non-democratic regimes ranging from China to Saudi Arabia have created domestic technological infrastructures, which undermine and provide an alternative to the core principles of the regime (Boas 2006; Deibert 2008).
The European Union, while still generally supportive of open communication and free speech, has grown skeptical of the regime’s focus on unfettered economic access and has used privacy and anti-trust policy to challenge its most neo-liberal elements (Newman 2008). Non-state actors like Wikileaks have relied on information openness as a channel of disruption and perhaps manipulation.
More troubling are the arguments of a new literature – that open information flows are less a harbinger of democracy than a vector of attack…
How can IR scholars make sense of this Janus-face quality of information? In this brief memo, we argue that much of the existing work on information technology and information flows suffers from two key deficiencies.
First – there has been an unhelpful separation between two important debates about information flows and liberalism. One – primarily focused on the international level – concerned global governance of information networks, examining how states (especially the US) arrived at and justified their policy stances, and how power dynamics shaped the battles between liberal and illiberal states over what the relevant governance arrangements should be (Klein 2002; Singh 2008; Mueller 2009). …
This leads to the second problem – that research has failed to appreciate the dynamics of contestation over time…(More)”
George Atalla at Ernst and Young: “Analysis of the success or failure of government digital transformation projects tends to focus on the technology that has been introduced. Seldom discussed is the role played by organizational culture and by a government’s willingness to embrace new approaches and working practices. And yet factors such as an ability to transcend bureaucratic working styles and collaborate with external partners are just as vital to success as deploying the right IT…
The study, Inside the Black Box: Journey Mapping Digital Innovation in Government, used a range of qualitative research tools including rich pictures, journey maps
The aim of the study was to look inside the “black box” of digital transformation to find out what really goes on within the teams responsible for delivery. In every case, the implementation journey involved ups and downs, advances and setbacks, but there were always valuable lessons to learn. We have extracted the six key insights for governments, outlined below, to provide guidance for government and public sector leaders who are embarking on their own innovation journey…(More)”.
Book edited by Carolin Kaltofen, Madeline Carr and Michele Acuto: “This book examines the role of technology in the core voices for International Relations theory and how this has shaped the contemporary thinking of ‘IR’ across some of the discipline’s major texts. Through an interview format between different generations of IR scholars, the conversations of the book analyse the relationship between technology and concepts like power, security and global order. They explore to what extent ideas about the role and implications of technology help to understand the way IR has been framed and world politics are conceived of today. This innovative text will appeal to scholars in Politics and International Relations as well as STS, Human Geography and Anthropology….(More)” .
Book edited by Aboul Ella Hassanien, Mohamed Elhoseny, Syed Hassan Ahmed and Amit Kumar Singh: “This book offers an essential guide to IoT Security, Smart Cities, IoT Applications, etc. In addition, it presents a structured introduction to the subject of destination marketing and an exhaustive review
Written in plain and straightforward language, the book offers a self-contained resource for readers with no prior background in the field. Primarily intended for students in Information Security and IoT applications (including smart cities systems and data heterogeneity), it will also greatly benefit academic researchers, IT professionals, policymakers and legislators. It is well suited as a reference book for both undergraduate and graduate courses on information security approaches, the Internet of Things, and real-world intelligent applications….(More)
Paper by Abhishek Nagaraj: “The public sector provides many types of information, such as geographic and census maps, that firms use when making decisions. However, the economic implications of such information infrastructure remain unexamined.
This study estimates the impact of information from Landsat, a NASA satellite mapping program, on the discovery of new deposits by large and small firms in the gold exploration industry. Using a simple theoretical framework, I argue that public sector information guides firms on the viability of risky projects and increases the likelihood of project success.
This effect is especially relevant for smaller firms, who face higher project costs and are particularly deterred from engaging in risky projects. I test the predictions of this framework by exploiting idiosyncratic timing variation in Landsat coverage across regions. Landsat maps nearly doubled the rate of significant gold discoveries after a region was mapped and increased the market share of smaller, junior firms from about 10% to 25%.
Public information infrastructure, including mapping efforts, seem to be an important, yet overlooked, driver of private-sector productivity and small business performance…(More)”