Blog post by Bridget Konadu Gyamfi and Bethany Park…:”Researchers are often invested in disseminating the results of their research to the practitioners and policymakers who helped enable it—but disseminating a paper, developing a brief, or even holding an event may not truly empower decision-makers to make changes based on the research. …
Disseminate results in stages and determine next steps
Mapping evidence to real-world decisions and processes in order to determine the right course of action can be complex. Together with our partners, we gather the troops—researchers, implementers, and IPA’s research and policy team—and have a discussion around what the implications of the research are for policy and practice.
This staged dissemination is critically important: having private discussions first helps partners digest the results and think through their reactions in a lower-stakes setting. We help the partners think about not only the results, but how their stakeholders will respond to the results, and how we can support their ongoing learning, whether results are “good” or not as hoped. Later, we hold larger dissemination events to inform the public. But we try to work closely with researchers and implementers to think through next steps right after results are available—before the window of opportunity passes.
Identify & prioritize policy opportunities
Many of our partners have already written smart advice about how to identify policy opportunities (windows, openings… etc.), so there’s no need for us to restate all that great thinking (go read it!). However, we get asked frequently how we prioritize policy opportunities, and we do have a clear internal process for making that decision. Here are our criteria:
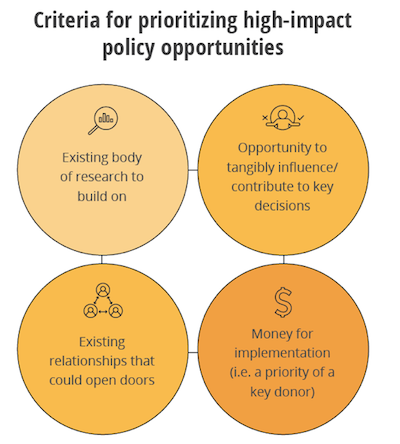
- A body of evidence to build on: One single study doesn’t often present the best policy opportunities. This is a generalization, of course, and there are exceptions, but typically our policy teams pay the most attention to bodies of evidence that are coming to a consensus. These are the opportunities for which we feel most able to recommend next steps related to policy and practice—there is a clearer message to communicate and research conclusions we can state with greater confidence.
- Relationships to open doors: Our long-term in-country presence and deep involvement with partners through research projects means that we have many relationships and doors open to us. Yet some of these relationships are stronger than others, and some partners are more influential in the processes we want to impact. We use stakeholder mapping tools to clarify who is invested and who has influence. We also track our stakeholder outreach to make sure our relationships stay strong and mutually beneficial.
- A concrete decision or process that we can influence: This is the typical understanding of a “policy opening,” and it’s an important one. What are the partner’s priorities, felt needs, and open questions? Where do those create opportunities for our influence? If the evidence would indicate one course of action, but that course isn’t even an option our partner would consider or be able to consider (for cost or other practical reasons), we have to give the opportunity a pass.
- Implementation funding: In the countries where we work, even when we have strong relationships, strong evidence, and the partner is open to influence, there is still one crucial ingredient missing: implementation funding. Addressing this constraint means getting evidence-based programming onto the agenda of major donors.
Get partners on board
Forming a coalition of partners and funders who will partner with us as we move forward is crucial. As a research and policy organization, we can’t scale effective solutions alone—nor is that the specialty that we want to