Bvudzai Magadzire, Melissa West, Emily Lawrence, Julia Guerette & Barbara Jones-Singer at the Stanford Social Innovation Review: ” …At the core of our framework is the idea that solutions must exist within an “enabling context.” The enabling context comprises external conditions such as a country’s level of political stability, government independence, and economic prosperity. Each of these can have a major effect on whether a government entity succeeds in sustaining a solution after an NGO or private-sector partner exits. While these external factors are generally outside most organizations’ control, monitoring them can inform decisions about how to invest time and resources, with the aim of minimizing their negative impacts on a government’s ability to sustain projects.
We are using tools like the PESTLE framework to help identify external factors that could impact the success of programs, as well as reviewing resources from USAID, World Bank, World Health Organization, and other agencies to better understand the political, economic, and social context for transitioning solutions to our government partners. For instance, the government of Malawi has made high-level political commitments to support maternal, adolescent, and child health, but as a low-income country, it has limited funds to spend on health. Thus, reducing costs is critical. VillageReach initially developed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) with the telecommunications provider Airtel—one of two major mobile service providers in Malawi. Since signing the MOU in 2015, Airtel has covered all incoming call and promotional text costs of the hotline, allowing callers to call CCPF for free from any Airtel phone. The government is now managing the MOU with Airtel as part of the transition process.
As organizations assess a social solution’s readiness for transition to government, they should consider both the external environment and each of the solution elements. (Illustration by The Medium)
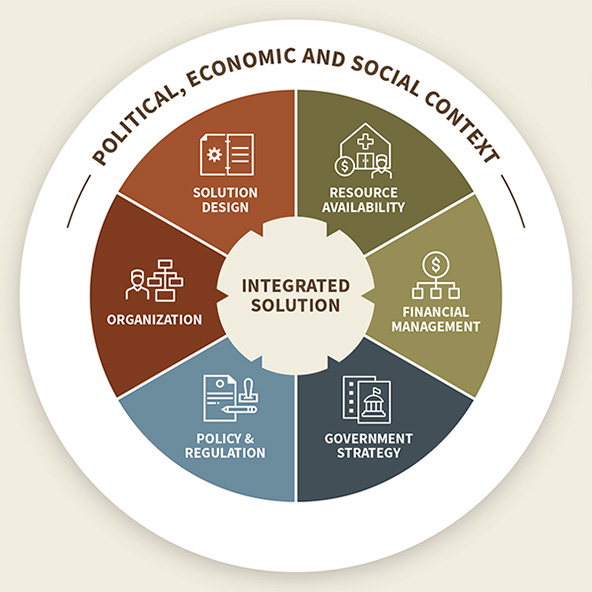
The second tier of our framework combines all the elements integral to a solution’s success that (unlike the enabling context) are within the control of an implementing organization. We call this the “integrated solution,” and it has six elements:
- Solution design: This includes standard operating procedures, guidelines, templates, and job and skill descriptions needed to manage and operate the solution. We are developing a toolkit specifically to support the government in managing CCPF.
- Resource availability: This includes the financial and human resources, as well as infrastructure like buildings and equipment, needed to transition, operate, and maintain the solution. For CCPF, we are supporting the development of a memorandum of understanding between the government and the telecommunications provider Airtel to ensure that the company continues to cover the costs of calls to the hotline.
- Financial management: This covers developing and managing budgets, estimating and managing costs, and disbursing funds in a timely fashion. This process has been important for understanding exactly which budgets need what amount of funds to ensure that operations continue.
- Government strategy: This includes sector (in our case, health-sector) and related government strategies that support the solution’s transition, operation, and maintenance. For CCPF, we needed to ensure that these aligned with Malawi’s broader strategic plan for the health sector.
- Policy and regulatory strategies: These are laws and regulations that affect the solution’s transition, operation, and maintenance. For CCPF, we needed to ensure that the cadre of hotline workers fit into government staffing protocols and that we could legally share certain types of health information with callers.
- Organizational structure: This includes managerial roles and responsibilities, management effectiveness, and governance. CCPF established a steering committee to help maintain alignment and accountability.
Organizations should evaluate and plan for the enabling context and integrated solution concurrently—ideally prior to or early on in the process of developing their solution, and periodically throughout its life….(More)”