Richard Wike and Alexandra Castillo at Pew Research Center: “An engaged citizenry is often considered a sign of a healthy democracy. High levels of political and civic participation increase the likelihood that the voices of ordinary citizens will be heard in important debates, and they confer a degree of legitimacy on democratic institutions. However, in many nations around the world, much of the public is disengaged from politics.
To better understand public attitudes toward civic engagement, Pew Research Center conducted face-to-face surveys in 14 nations encompassing a wide range of political systems. The study, conducted in collaboration with the Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS) as part of their International Consortium on Closing Civic Space (iCon), includes countries from Africa, Latin America, Europe, the Middle East and Southeast Asia. Because it does not represent every region, the study cannot reflect the globe as a whole. But with 14,875 participants across such a wide variety of countries, it remains a useful snapshot of key, cross-national patterns in civic life.
The survey finds that, aside from voting, relatively few people take part in other forms of political and civic participation. Still, some types of engagement are more common among young people, those with more education, those on the political left and social network users. And certain issues – especially health care, poverty and education – are more likely than others to inspire political action. Here are eight key takeaways from the survey, which was conducted from May 20 to Aug. 12, 2018, via face-to-face interviews.
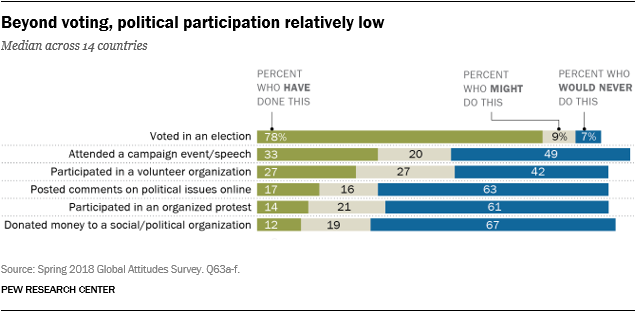
Most people vote, but other forms of participation are much less common. Across the 14 nations polled, a median of 78% say they have voted at least once in the past. Another 9% say they might vote in the future, while 7% say they would never vote.
With at least 9-in-10 reporting they have voted in the past, participation is highest in three of the four countries with compulsory voting (Brazil, Argentina and Greece). Voting is similarly high in both Indonesia (91%) and the Philippines (91%), two countries that do not have compulsory voting laws.
The lowest percentage is found in Tunisia (62%), which has only held two national elections since the Jasmine Revolution overthrew long-serving President Zine El Abidine Ben Ali in 2011 and spurred the Arab Spring protests across the Middle East.
Attending a political campaign event or speech is the second most common type of participation among those surveyed – a median of 33% have done this at least once. Fewer people report participating in volunteer organizations (a median of 27%), posting comments on political issues online (17%), participating in an organized protest (14%) or donating money to a social or political organization (12%)….(More)”.