Open Corporates: “…there are three other aspects which are relevant when talking about access to EU company data.
Cargo-culting GDPR
The first, is a tendency to take this complex and subtle legislation that is GDPR and use a poorly understood version in other legislation and regulation, even if that regulation is already covered by GDPR. This actually undermines the GDPR regime, and prevents it from working effectively, and should strongly be resisted. In the tech world, such approaches are called ‘cargo-culting’.
Similarly GDPR is often used as an excuse for not releasing company information as open data, even when the same data is being sold to third parties apparently without concerns — if one is covered by GDPR, the other certainly should be.
Widened power asymmetries
The second issue is the unintended consequences of GDPR, specifically the way it increases asymmetries of power and agency. For example, something like the so-called Right To Be Forgotten takes very significant resources to implement, and so actually strengthens the position of the giant tech companies — for such companies, investing millions in large teams to decide who should and should not be given the Right To Be Forgotten is just a relatively small cost of doing business.
Another issue is the growth of a whole new industry dedicated to removing traces of people’s past from the internet (2), which is also increasing the asymmetries of power. The vast majority of people are not directors of companies, or beneficial owners, and it is only the relatively rich and powerful (including politicians and criminals) who can afford lawyers to stifle free speech, or remove parts of their past they would rather not be there, from business failures to associations with criminals.
OpenCorporates, for example, was threatened with a lawsuit from a member of one of the wealthiest families in Europe for reproducing a gazette notice from the Luxembourg official gazette (a publication that contains public notices). We refused to back down, believing we had a good case in law and in the public interest, and the other side gave up. But such so-called SLAPP suits are becoming increasingly common, although unlike many US states there are currently no defences in place to resist these in the EU, despite pressure from civil society to address this….
At the same time, the automatic assumption that all Personally Identifiable Information (PII), someone’s name for example, is private is highly problematic, confusing both citizens and policy makers, and further undermining democracies and fair societies. As an obvious case, it’s critical that we know the names of our elected representatives, and those in positions of power, otherwise we would have an opaque society where decisions are made by nameless individuals with opaque agendas and personal interests — such as a leader awarding a contract to their brother’s company, for example.
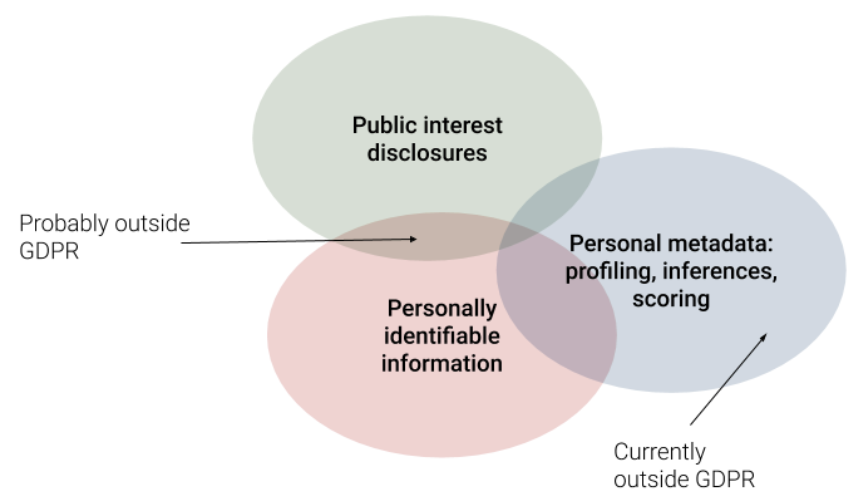
As the diagram below illustrates, there is some personally identifiable information that it’s strongly in the public interest to know. Take the director or beneficial owner of a company, for example, of course their details are PII — clearly you need to know their name (and other information too), otherwise what actually do you know about them, or the company (only that some unnamed individual has been given special protection under law to be shielded from the company’s debts and actions, and yet can benefit from its profits)?
On the other hand, much of the data which is truly about our privacy — the profiles, inferences and scores that companies store on us — is explicitly outside GDPR, if it doesn’t contain PII.
Hopefully, as awareness of the issues increases, we will develop a more nuanced, deeper, understanding of privacy, such that case law around GDPR, and successors to this legislation begin to rebalance and case law starts to bring clarity to the ambiguities of the GDPR….(More)”.