FastCoExist: “Most kids learn the grade school civics lesson about how a bill becomes a law. What those lessons usually neglect to show is how legislation today is often birthed on a lobbyist’s desk.
But even for expert researchers, journalists, and government transparency groups, tracing a bill’s lineage isn’t easy—especially at the state level. Last year alone, there were 70,000 state bills introduced in 50 states. It would take one person five weeks to even read them all. Groups that do track state legislation usually focus narrowly on a single topic, such as abortion, or perhaps a single lobby groups.
Computers can do much better. A prototype tool, presented in September at Bloomberg’sData for Good Exchange 2015 conference, mines the Sunlight Foundation’s database of more than 500,000 bills and 200,000 resolutions for the 50 states from 2007 to 2015. It also compares them to 1,500 pieces of “model legislation” written by a few lobbying groups that made their work available, such as the conservative group ALEC (American Legislative Exchange Council) and the liberal group the State Innovation Exchange(formerly called ALICE).
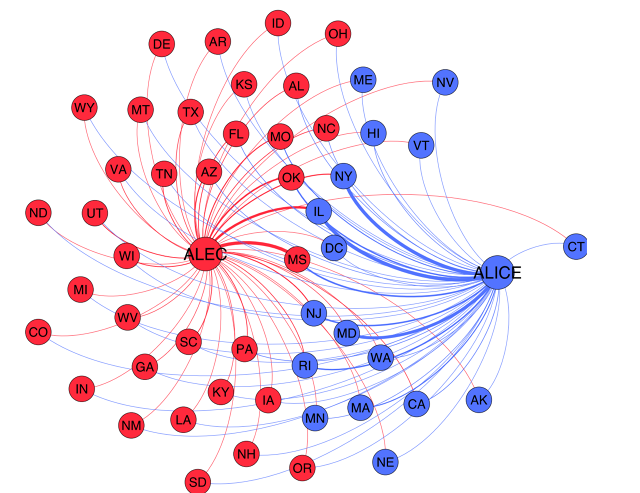
The results are interesting. In one example of the program in use, the team—all from the Data Science for Social Good fellowship program in Chicago—created a graphic (above) that presents the relative influence of ALEC and ALICE in different states. The thickness of each line in the graphic correlates to the percentage of bills introduced in each state that are modeled on either group’s legislation. So a relatively liberal state like New York is mostly ALICE bills, while a “swing” state like Illinois has a lot from both groups….
Along with researchers from the University of Chicago, Wikimedia Foundation, Microsoft Research, and Northwestern University, Walsh is also co-author of another paperpresented at the Bloomberg conference shows how data science can increase government transparency.
Walsh and these co-authors developed software that automatically identifies earmarks in U.S. Congressional bills, showing how representatives are benefiting their own states with pork barrel projects. They verified that it works by comparing it to the results of a massive effort from the U.S. Office of Management and Budget to analyze earmarks for a few limited years. Their results, extended back to 1995 in a public database, showed that there may be many more earmarks than anyone thought.
“Governments are making more data available. It’s something like a needle in a haystack problem, trying to extract all that information out,” says Walsh. “Both of these projects are really about shining light to these dark places where we don’t know what’s going on.”
The state legislation tracker data is available for download here, and the team is working on an expanded system that automatically downloads new state legislation so it can stay up to date…(More)”