Kriss Deiglmeier & Amanda Greco at Stanford Social Innovation Review: “…As we applied the innovation continuum to the cases we studied, we identified barriers to scale that often trap social innovations in a stagnation chasm before they achieve diffusion and scaling.
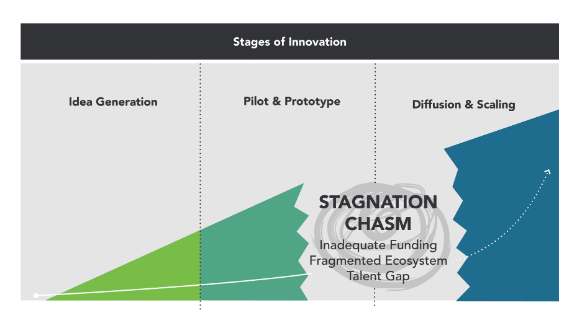
Three barriers in particular repeatedly block social innovations from reaching their broadest impact: inadequate funds for growth, the fragmented nature of the social innovation ecosystem, and talent gaps. If we are serious about propelling proven social innovations to achieve widespread impact, we must find solutions that overcome each of these barriers. The rest of the article will explore in more detail each of these three barriers in turn.
1. Inadequate Funding
Social innovators face a convoluted and often elusive path to mobilize the resources needed to amplify the impact of their work. Of the strategies for scale in Mulgan’s typology, some are very capital intensive, others less so. Yet even the advocacy and network approaches to scaling social impact require resources. It takes time, funding, and expertise to navigate the relationships and complex interdependencies that are critical to success. Some ventures may benefit from earned revenue streams that provide funds for growth, but earned revenue isn’t guaranteed in the social innovation space, especially for innovations that operate where markets fail to meet needs and serve people with no ability to pay. Thus, external funding is usually needed in order to scale impact, whether from donors or from investors depending on the legal structure and financial prospects of the venture….
2. A Fragmented Ecosystem
One sector toiling in isolation or digging into an adversarial approach cannot achieve breakthrough scale on its own. Instead, engaging and coordinating actions across various actors from the private, nonprofit, and public sectors is critical. In the case of microfinance, for example, the innovation garnered interest from government and business when nonprofits like Grameen Bank had demonstrated success in providing financial services to formerly unbanked people.
Following the pioneering role of nonprofits to establish proof of concept, commercial banks entered the market, with mixed social outcomes, given the pressure they faced for profitability. As the microfinance industry matured, governments created a legal and regulatory environment that encouraged transparency, market entry, and competition. The cumulative efforts and engagement across the nonprofit, private, and public sectors were critical to scaling microfinance as we know it today and will continue to refine the approach for better social outcomes in the future…
3. The Talent Gap
To drive social innovations in a world of rapid change, organizations need talented leaders supported by effective teams. The insufficient funding and fragmented ecosystem require highly adept people to shepherd social innovations through the long journey to widespread social impact. Unfortunately, attracting and retaining people to navigate these complexities is a challenge…(More)”.