Manuel León Urrutia at The Conversation: “I find it tempting to celebrate the public’s expanding access to data and familiarity with terms like “flattening the curve”. After all, a better informed society is a successful society, and the provision of data-driven information to the public seems to contribute to the notion that together we can beat COVID.
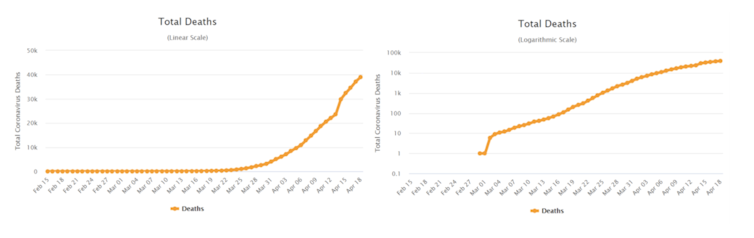
But increased data visibility shouldn’t necessarily be interpreted as increased data literacy. For example, at the start of the pandemic it was found that the portrayal of COVID deaths in logarithmic graphs confused the public. Logarithmic graphs control for data that’s growing exponentially by using a scale which increases by a factor of ten on the y, or vertical axis. This led some people to radically underestimate the dramatic rise in COVID cases.
The vast amount of data we now have available doesn’t even guarantee consensus. In fact, instead of solving the problem, this data deluge can contribute to the polarisation of public discourse. One study recently found that COVID sceptics use orthodox data presentation techniques to spread their controversial views, revealing how more data doesn’t necessarily result in better understanding. Though data is supposed to be objective and empirical, it has assumed a political, subjective hue during the pandemic….
This is where educators come in. The pandemic has only strengthened the case presented by academics for data literacy to be included in the curriculum at all educational levels, including primary. This could help citizens navigate our data-driven world, protecting them from harmful misinformation and journalistic malpractice.
Data literacy does in fact already feature in many higher education roadmaps in the UK, though I’d argue it’s a skill the entire population should be equipped with from an early age. Misconceptions about vaccine efficacy and the severity of the coronavirus are often based on poorly presented, false or misinterpreted data. The “fake news” these misconceptions generate would spread less ferociously in a world of data literate citizens.
To tackle misinformation derived from the current data deluge, the European Commission has funded projects such as MediaFutures and YourDataStories….(More)”.

