Paper by Joy Hsu, Ramya Ravichandran, Edwin Zhang, and Christine Keung: “There is an increasing need for open data in governments and systems to analyze equity at large scale. Local governments often lack the necessary technical tools to identify and tackle inequities in their communities. Moreover, these tools may not generalize across departments and cities nor be accessible to the public. To this end, we propose a system that facilitates centralized analyses of publicly available government datasets through 1) a US Census-linked API, 2) an equity analysis playbook, and 3) an open data standard to regulate data intake and support equitable policymaking….(More)”.
Design for Social Innovation: Case Studies from Around the World
Book edited By Mariana Amatullo, Bryan Boyer, Jennifer May and Andrew Shea: “The United Nations, Australia Post, and governments in the UK, Finland, Taiwan, France, Brazil, and Israel are just a few of the organizations and groups utilizing design to drive social change. Grounded by a global survey in sectors as diverse as public health, urban planning, economic development, education, humanitarian response, cultural heritage, and civil rights, Design for Social Innovation captures these stories and more through 45 richly illustrated case studies from six continents.
From advocating to understanding and everything in between, these cases demonstrate how designers shape new products, services, and systems while transforming organizations and supporting individual growth.
How is this work similar or different around the world? How are designers building sustainable business practices with this work? Why are organizations investing in design capabilities? What evidence do we have of impact by design? Leading practitioners and educators, brought together in seven dynamic roundtable discussions, provide context to the case studies.
Design for Social Innovation is a must-have for professionals, organizations, and educators in design, philanthropy, social innovation, and entrepreneurship. This book marks the first attempt to define the contours of a global overview that showcases the cultural, economic, and organizational levers propelling design for social innovation forward today…(More)”
Data for Children Collaborative Designs Responsible Data Solutions for Cross-Sector Services
Impact story by data.org: “That is the question that the Collaborative set out to answer: how do we define and support strong data ethics in a way that ensures it is no longer an afterthought? How do we empower organizations to make it their priority?…
Fassio, Data for Children Collaborative Director Alex Hutchison, and the rest of their five-person team set out to create a roadmap for data responsibility. They started with their own experiences and followed the lifecycle of a non-profit project from conception to communicating results.
The journey begins – for project leaders and for the Collaborative – with an ethical assessment before any research or intervention has been conducted. The assessment calls on project teams to reflect on their motivations and ethical issues at the start, midpoint, and results stages of a project, ensuring that the priority stakeholder remains at the center. Some of the elements are directly tied to data, like data collection, security, and anonymization, but the assessment goes beyond the hard data and into its applications and analysis, including understanding stakeholder landscape and even the appropriate language to use when communicating outputs.
For the Collaborative, that priority is children. But they’ve designed the assessment, which maps across to UNICEF’s Responsible Data for Children (RD4C) toolkit, and other responsible innovation resources to be adaptable for other sectors.
“We wanted to make it really accessible for people with no background in ethics or data. We wanted anyone to be able to approach it,” Fassio said. “Because it is data-focused, there’s actually a very wide application. A lot of the questions we ask are very transferable to other groups.”
The same is true for their youth participation workbook – another resource in the toolkit. The team engaged young people to help co-create the process, staying open to revisions and iterations based on people’s experiences and feedback….(More)”
Morocco finds a new source of policy expertise — its own citizens
Participo: “This spring saw the release of a long-awaited report by the Commission Spéciale sur le modèle de developpement (CSMD), created in 2019 by His Majesty King Mohammed VI….
“Blue ribbon” commissions to tackle thorny issues are nothing new. But the methods employed by Morocco’s CSMD, and the proposals which resulted from them, point the way toward an entirely new approach to governance in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region.
Morocco’s new model of development was created through methods of collective intelligence, an emerging science that explores how groups can outperform individuals in learning, decision making, and problem-solving.
It is an ability that has long defined our species, from coordinated bands of hunters on the savannah to the networks of scientists that develop coronavirus vaccines. A complex environment has conditioned humans to pool their knowledge to survive. But collective intelligence doesn’t just happen; for the “wisdom of crowds” to emerge, a group must be organized in the right way, with the right methods and tools….
Beginning in January 2020, the CSMD launched a broad national consultation open to all Moroccan citizens, aimed at harnessing a wide variety of expertise from local communities, government, NGOs, and the private sector.
Its multi-channel approach was designed to reflect four indicators that studies suggest are critical to producing collective intelligence: a diversity of participants and information sources; a critical mass of contributions; a sufficiently rich exchange of information at each “touch point”; and an effective process to synthesize contributions into a coherent whole.
The CSMD created an online platform with opportunities to give quick feedback (“What is one thing you want to change about Morocco?”), as well as more detailed proposals on themes like health care and territorial inequality. A social media campaign reached an estimated 3.2 million citizens, with dozens of “participatory workshops” live-streamed on Facebook and YouTube.
To seek out the knowledge of those least connected to these channels, the CSMD conducted 30 field visits to struggling urban districts, universities, and remote villages in the High Atlas mountains. These field visits featured learning sessions with social innovators and rencontres citoyennes (“citizen encounters”) where groups of 20 to 30 local residents, balanced by age and gender, shared stories and aspirations….(More)”.
The Secret Bias Hidden in Mortgage-Approval Algorithms
An investigation by The Markup: “…has found that lenders in 2019 were more likely to deny home loans to people of color than to White people with similar financial characteristics—even when we controlled for newly available financial factors that the mortgage industry for years has said would explain racial disparities in lending.
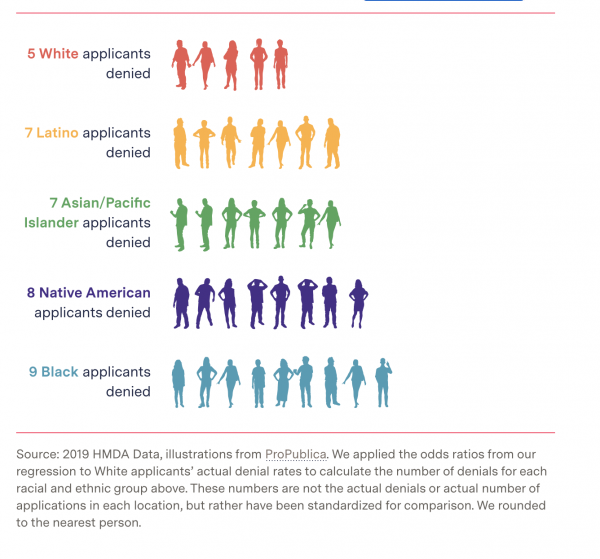
Holding 17 different factors steady in a complex statistical analysis of more than two million conventional mortgage applications for home purchases, we found that lenders were 40 percent more likely to turn down Latino applicants for loans, 50 percent more likely to deny Asian/Pacific Islander applicants, and 70 percent more likely to deny Native American applicants than similar White applicants. Lenders were 80 percent more likely to reject Black applicants than similar White applicants. These are national rates.
In every case, the prospective borrowers of color looked almost exactly the same on paper as the White applicants, except for their race.
The industry had criticized previous similar analyses for not including financial factors they said would explain disparities in lending rates but were not public at the time: debts as a percentage of income, how much of the property’s assessed worth the person is asking to borrow, and the applicant’s credit score.
The first two are now public in the Home Mortgage Disclosure Act data. Including these financial data points in our analysis not only failed to eliminate racial disparities in loan denials, it highlighted new, devastating ones.
We found that lenders gave fewer loans to Black applicants than White applicants even when their incomes were high—$100,000 a year or more—and had the same debt ratios. In fact, high-earning Black applicants with less debt were rejected more often than high-earning White applicants who have more debt….(More)”
Government transformations in times of extraordinary change: Key considerations for public-sector leaders
Article by Scott Blackburn, Thomas Harrington, Andrea Vidler, and Brooke Weddle: “Enacting major change in large, matrixed government organizations is always a challenge, with the COVID-19 pandemic adding another layer of complexity. Although just 20 percent of public-sector transformations meet their objectives, an equal focus on improving both performance and organizational health improves the odds of success by as much as 79 percent.
Maintaining a dual focus on performance and organizational health (see sidebar, “Defining performance and organizational health”) is even more important during periods of immense change. Leaders in high-pressure situations and rapidly changing environments may find themselves focusing on performance and neglecting organizational health. The leadership team may not understand the full value of investing in organizational health, the right resources may not be allocated to it, or leaders may simply lack the capabilities and experience needed to address it. But when leaders fail to address organizational health, they fail to help their agencies reach their full potential for performance….
Define and implement a bold performance agenda
Government leaders are under intense pressure to rapidly deliver better performance for their constituents at a low cost—all within a high-stakes, often opaque environment of unprecedented change. Our experience indicates that the most successful transformations include the following four elements.
Aspirational goals. When leaders set goals that are aspirational—those that seek to achieve an organization’s full potential—performance gains are higher. Bold goals set using internal and external performance benchmarks force organizations to think differently and inspirationally and to move beyond the normal incrementalism that marks yearly budget planning or strategy setting. Once set, these aspirational goals can be shared widely and transparently across the organization—at employee town-hall meetings, in senior-leadership meetings, and on message boards and computer screens throughout the office—to increase buy-in and translate to clear and measurable benchmarks for all staff. Top leaders should also genuinely commit themselves and their organizations to achieving the targets.
Balanced portfolio of pragmatic initiatives. Aspirational goals will guide the changes to come. The best transformations provide opportunities for hundreds of people across the organization to identify and implement concrete performance improvements. Initiatives will help achieve the aspirational goals and can be filtered based on priority—What should we accomplish this quarter? What can we push to next quarter to ensure our focus remains on the top priorities?—and then tied to initiative owners who will drive them to completion. Senior leaders can then commit to supporting initiative owners as sponsors who remove roadblocks and coaches who expedite decision making.
Execution ‘engine.’ Leaders can set a series of regularly scheduled meetings, weekly or monthly, to focus on reviewing performance and results, taking care to go beyond progress on activities. This engine provides a regular and open channel for teams to elevate key issues, get to the heart of problems, and build a forum for low-stakes dialogue. The most successful organizations have a regular rhythm to these meetings and focus on reviewing whether teams are achieving results, what can be done to move faster and work more effectively, and what barriers need to be removed…(More)”.
How Does Participatory Action Research Generate Innovation? Findings from a Rapid Realist Review
Report by Mieke Snijder and Marina Apgar: “A rapid realist review was undertaken to develop programme theories that explain how PAR generates innovation. The methodology included peer-reviewed and grey literature and moments of engagement with programme staff, such that their input supported the development and refinement of three resulting initial programme theories (IPTs) that we present in this report. Across all three IPTs, safe relational space, group facilitation, and the abilities of facilitators, are essential context and intervention components through which PAR can generate innovation. Implications from the three IPTs for evaluation design of the CLARISSA programme are identified and discussed. The report finishes with opportunities for the CLARISSA programme to start building an evidence base of how PAR works as an intervention modality, such as evidencing group-level conscientisation, the influence of intersecting inequalities, and influence of diverse perspectives coming together in a PAR process….(More)”.
Chinese web users are writing a new playbook for disaster response
Shen Lu at Protocol: Severe floods caused by torrential rains in Central China’s Henan province have killed dozens and displaced tens of thousands of residents since last weekend. In parallel with local and central governments’ disaster relief and rescue efforts, Chinese web users have organized online, using technology in novel ways to mitigate risks and rescue those who were trapped in subway cars and neighborhoods submerged in floodwaters.
Chinese web users are no strangers to digital crowdsourcing efforts. During the COVID-19 outbreak, volunteers archived censored media reports and personal stories of suffering from disease or injustice that were scattered on social media, saving them on sharable files on GitHub and broadcasting them via Telegram. Despite pervasive censorship, in times of crisis, Chinese web users have managed to keep information and communications channels open among themselves, and with the rest of the world.
Now, people in one of the most oppressive information environments in the world might be helping write the future playbook for disaster response…
In hard-hit Zhengzhou, the capital city of Henan province, tens of thousands of residents crowdsourced relief assistance over the past 48 hours through a simple shared spreadsheet powered by the Tencent equivalent of Google Sheets (Google products are banned in China). It was created by a college student to allow those awaiting rescue to log their contact and location information.
In the 36 hours that followed, droves of volunteers have logged on, vastly expanding the breadth of information that lives on the document. It now includes contact information for official and unofficial rescue teams, relief resources, shelter locations, phone-charging stations and online medical consultations. At certain points, over 200 people have edited the sheet simultaneously.
Tencent reported that by Wednesday evening Beijing time, volunteers had entered nearly 1,000 data points. The document has received over 2.5 million visits, becoming the most visited Tencent Doc ever and one of the most efficient and powerful rescue and aid platforms started and contributed by civilians.
Similar crowdsourced documents for flooding victims live elsewhere on the internet. On Shimo Docs, a cloud-based productivity suite developed by the Beijing-based startup Shimo, volunteers have aggregated relief and rescue resources’ contacts by cities and counties. These shared documents have made the rounds on social media platforms like Weibo and WeChat in the past few days….(More)”.
Data Literacy in Government: How Are Agencies Enhancing Data Skills?
Randy Barrett at FedTech: “The federal government is vast, and the challenge of understanding its oceans of data grows daily. Rather than hiring thousands of new experts, agencies are moving to train existing employees on how to handle the new frontier.
Data literacy is now a common buzzword, spurred by the publication of the Federal Data Strategy 2020 Action Plan last year and the growing empowerment of chief data officers in the government. The document outlines a multiyear, holistic approach to government information that includes building a culture that values data, encouraging strong management and protection and promoting its efficient and appropriate use.
“While the Federal government leads globally in many instances in developing and providing data about the United States and the world, it lacks a robust, integrated approach to using data to deliver on mission, serve the public and steward resources,” the plan notes.
A key pillar of the plan is to “identify opportunities to increase staff data skills,” and it directs all federal agencies to undertake a gap analysis of skills to see where the weaknesses and needs lie….
The Department of Health and Human Services launched its Data Science CoLab in 2017 to boost basic and intermediate data skills. The collaborative program is the first try at a far reaching and cohort-based data-skills training for the agency. In addition to data analytics skills, HHS is currently training hundreds of employees on how to write Python and R.
“Demand for a seat in the Data Science CoLab has grown approximately 800 percent in the past three years, a testament to its success,” says Bishen Singh, a senior adviser in the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Health. “Beyond skill growth, it has led to incredible time and cost savings, as well as internal career growth for past participants across the department.”
The National Science Foundation was less successful with its Data Science and Data Certification Pilot, which had a class of 10 participants from various federal agencies. The workers were trained in advanced analytics techniques, with a focus on applying data tools to uncover meaning and solve Big Data challenges. However, the vendor curriculum used general data sets rather than agency-specific ones.
“As a result, participants found it more difficult to apply their learnings directly to real-world scenarios,” notes the CDO Council’s “Data Skill Training Program: Case Studies” report. The learning modules were mostly virtual and self-paced. Communication was poor with the vendor, and employees began to lag in completing their coursework. The pilot was discontinued.
Most of the training pilot programs were launched as the pandemic closed down government offices. The shift to virtual learning made progress difficult for some students. Another key lesson: Allow workers to use their new skills quickly, while they’re fresh….(More)”.
Big data for economic statistics
Stats Brief by ESCAP: “This Stats Brief gives an overview of big data sources that can be used to produce economic statistics and presents country examples of the use of online price data, scanner data, mobile phone data, Earth Observations, financial transactions data and smart meter data to produce price indices, tourism statistics, poverty estimates, experimental economic statistics during COVID-19 and to monitor public sentiment. The Brief is part of ESCAP’s series on the use of non-traditional data sources for official statistics….(More)”.
