Aaron Smith, Laura Silver, Courtney Johnson, Kyle Taylor and Jingjing Jiang at Pew Research: “In recent years, the internet and social media have been integral to political protests, social movements and election campaigns around the globe. Events from the Arab Spring to the worldwide spread of#MeToo have been aided by digital connectivity in both advanced and emerging economies. But popular social media and messaging platforms like Facebook and WhatsApp have drawn attention for their potential role in spreading misinformation, facilitating political manipulation by foreign and domestic actors, and increasing violence and hate crimes.
Recently, the Sri Lankan government shut down several of the country’s social media and messaging services immediately after Easter day bombings at Catholic churches killed and wounded hundreds. Some technology enthusiasts praised the decision but wondered if this development marked a change from pro-democracy, Arab Spring-era hopes that digital technology would be a liberating tool to a new fear that it has become “a force that can corrode” societies.
In the context of these developments, a Pew Research Center survey of adults in 11 emerging economies finds these publics are worried about the risks associated with social media and other communications technologies – even as they cite their benefits in other respects. Succinctly put, the prevailing view in the surveyed countries is that mobile phones, the internet and social media have collectively amplified politics in both positive and negative directions – simultaneously making people more empowered politically andpotentially more exposed to harm.
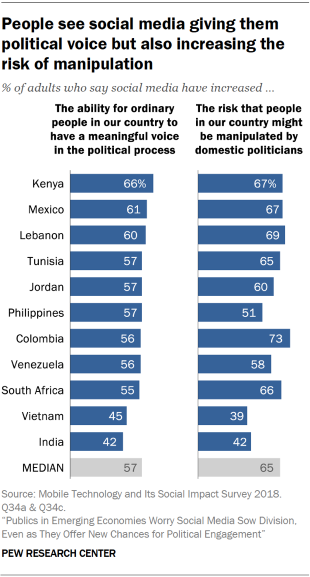
When it comes to the benefits, adults in these countries see digital connectivity enhancing people’s access to political information and facilitating engagement with their domestic politics. Majorities in each country say access to the internet, mobile phones and social media has made people more informed about current events, and majorities in most countries believe social media have increased ordinary people’s ability to have a meaningful voice in the political process. Additionally, half or more in seven of these 11 countries say technology has made people more accepting of those who have different views than they do.
But these perceived benefits are frequently accompanied by concerns about the limitations of technology as a tool for political action or information seeking. Even as many say social media have increased the influence of ordinary people in the political process, majorities in eight of these 11 countries feel these platforms have simultaneously increased the risk that people might be manipulated by domestic politicians. Around half or more in eight countries also think these platforms increase the risk that foreign powers might interfere in their country’s elections….(More)”.