Bloomberg Cities: “…Three open data approaches cities are finding success with:
Map it
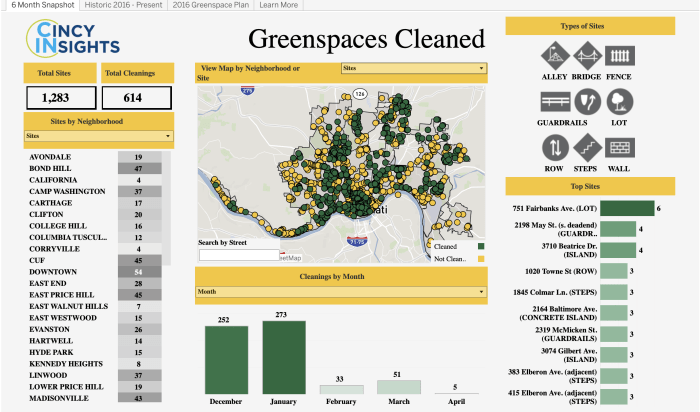
Much of the data that people seem to be most interested in is location-based, local data leaders say. That includes everything from neighborhood crime stats and police data used by journalists and activists to property data regularly mined by real estate companies. Rather than simply making spatial data available, many cities have begun mapping it themselves, allowing users to browse information that’s useful to them.
At atlas.phila.gov, for example, Philadelphians can type in their own addresses to find property deeds, historic photos, nearby 311 complaints and service requests, and their polling place and date of the next local election, among other information. Los Angeles city’s GeoHub collects maps showing the locations of marijuana dispensaries, reports of hate crimes, and five years of severe and fatal crashes between drivers and bikers or pedestrians, and dozens more.
….
Train residents on how to use it
Cities with open-data policies learn from best practices in other city halls. In the last few years, many have begun offering trainings to equip residents with rudimentary data analysis skills. Baton Rouge, for example, offered a free, three-part Citizen Data Academy instructing residents on “how to find [open data], what it includes, and how to use it to understand trends and improve quality of life in our community.” …
In some communities, open-data officials work with city workers and neighborhood leaders to learn to help their communities access the benefits of public data even if only a small fraction of residents are accessing the data itself.
In Philadelphia, city teams work with the Citizens Planning Institute, an educational initiative of the city planning commission, to train neighborhood organizers in how to use city data around things like zoning and construction permits to keep up with development in their neighborhoods, says Kistine Carolan, open data program manager in the Office of Innovation and Technology. The Los Angeles Department of Neighborhood Empowerment runs a Data Literacy Program to help neighborhood groups make better use of the city’s data. So far, officials say, representatives of 50 of the city’s 99 neighborhood councils have signed up as part of the Data Liaisons program to learn new GIS and data-analysis skills to benefit their neighborhoods.
Leverage the COVID moment
The COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted cities’ open-data plans, just like it has complicated every other aspect of society. Cities had to cancel scheduled in-person trainings and programs that help them reach some of their less-connected residents. But the pandemic has also demonstrated the fundamental role that data can play in helping to manage public emergencies. Cities large and small have hosted online tools that allow residents to track where cases are spiking—tools that have gotten many new people to interact with public data, officials say….(More)”.
