Darrell Etherington at TechCrunch: “Uber is opening up in an area where it might make sense competitively for it to stay more closed off: The ride-hailing company’s new Movement website will offer up access to its data around traffic flow in scores where it operates, intended for use by city planners and researchers looking into ways to improve urban mobility.
The basic idea is that Uber has a lot of insight into how traffic works within a city, and it can anonymize this data so that it isn’t tied to specific individuals in most cases. So where that’s possible, Uber is going to begin sharing said data, first to specific organizations who apply for early access, and then eventually to the general public.
Uber says it was looking at all the data it gathered and began to realize that it could be used for public benefit, and assembled a product team to make this happen. The result of this effort was Movement, which aims to address problems city officials and urban planners encounter when they’re forced to make key, transformational infrastructure decisions without access to all of, or the proper information about actual conditions and causes.
Essentially, according to Uber, it’s hoping to make it easier for those with influence over a city’s transportation picture to make the right decision, and to be able to explain why, where and when the changes are happening with accurate data backing them up. It also wants to do this in a way that makes it easy for organizations to work with, so it’s releasing the data organized around traffic analysis zones within cities, which are agreed-upon geographic demarcations that help with existing urban planning and traffic management.
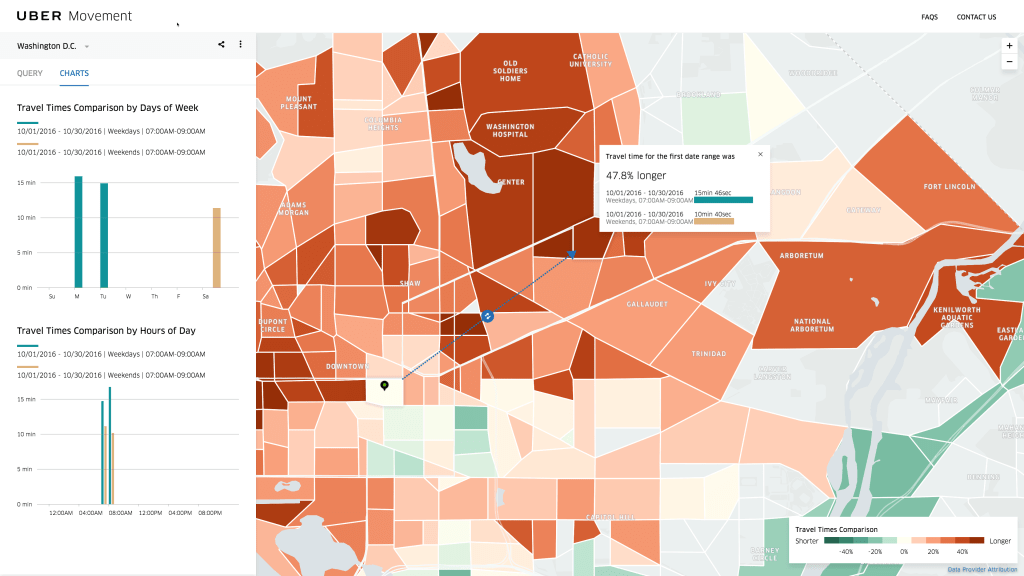
Users of the website can adjust things like time of day, day of week and zones to call up Uber’s data for that specific point or range, and can download the data, both with existing time series charts and in raw format for inputting into their own models. Uber says it’s looking at also releasing access to the data as an API, but is “trying to figure out how to do it in a performant way” at this stage….(More)”
