Sir Tim Berners-Lee; ” I was recently asked to talk about the idea of “open”, and I realized the term is used in at least eight different ways. The distinct interpretations are all important in different but interlocking ways. Getting them confused leads to a lot of misunderstanding, so it’s good to review them all.
When we tease apart their meanings, we can understand more clearly which aspects of each are the most important. The first, one of the most important forms of openness for the Web, is its universality.
Universality – When I designed the Web protocols, I had already seen many networked information systems fail because they made some assumptions about the users – that they were using a particular type of computer for instance – or constrained the way they worked, such as forcing them to organize their data in a particular way, or to use a particular data format. The Web had to avoid these issues. The goal was that anyone should be able to publish anything on the Web and so it had to be universal in that it was independent of all these technical constraints, as well as language, character sets, and culture….
Open Standards
The actual design of the Web involved the creation of open standards – and getting people to agree to use them globally. The World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), of which I am the Director, helps create interoperable standards for Web technology, including HTML5, mobile Web, graphics, the Semantic Web of linked data, and Web accessibility. Any company can join and anyone can review and help create the specifications for the Web….
Open Web Platform (OWP)
W3C’s Open Web Platform is the name for a particular set of open standards which enable an exciting stage of Web computing. Standards such as HTML5, SVG, CSS, video, JavaScript, and others are advancing together so that programmes that once worked only on desktop, tablets or phones can now work from within the browser itself. It has all the power of HTML5, like easily-inserted video and, in the future, easily-inserted conferences. It also features the APIs for accessing hardware and other capabilities on the device, such as a smartphone’s accelerometer, camera, and local storage. While native apps are limited, Web Apps can work on any platform….
Open Government through Open Data
In 2009, I resolved to encourage more use of data on the Web. Too many websites could generate nice reports as documents, but had no way to access the data behind it to check and build on the results. In February that year I stood up in front of a TED audience and asked them for their data; I even got them to chant: “raw data now”. In April that year, I met with Gordon Brown, then Prime Minister of the UK and with him began the UK Government’s ground-breaking work on Open Data. That same year President Barack Obama announced his commitment to the US Open Government Initiative. In 2010 I went back to TED and showed the audience some of what had been achieved, including Open Street Map’s role in relief efforts in Haiti….
Open Platform
While it’s not really a feature of the Web, a concern for a lot of people is whether they can choose which apps run on their own phone or computer. An Open Platform means having the right to install and write software on your computer or device. One motivation to close off a computing platform comes from a manufacturer wanting to allow you to experience their content on your machine without being able to store it or pass it on. Some systems are very closed, in that the user can only watch a movie or play a game, with no chance to copy anything or back it up. Some systems are very open, allowing users to take copies of files and run any application they like. Many systems fall in between, letting users pay for additional material or an experience…
Open Source
“Open Source” is another way “open” is used on the web, one which has been and is very important to the Web’s growth. It’s important to me that I can get at the source code of any software I’m using. If I can get at the source code, can I modify it? Can I distribute the modified code and run it on my machine? As Free Software Foundation lead Richard Stallman puts it, “free as in freedom rather than free as in beer”.
Open Access
Open Access is a Web-based movement specifically about free (as in beer) access to the body of academic learning. Governments, and therefore taxpayers, pay for research via grants but often the results of the research are kept in closed-access academic journals. The results are only available to those at big universities. The poor and those in remote rural areas cannot participate…
Open Internet and Net Neutrality
When we talk about keeping the internet free and open, we are often worried about blocking and spying. One of the ways in which we protect the Web is by ensuring Net Neutrality. Net Neutrality is about non-discrimination. Its principle is that if I pay to connect to the Net with a certain quality of service, and you pay to connect with that or a greater quality of service, then we can both communicate at the same level. This is important because it allows an open, fair market. It’s essential to an open, fair democracy. The alternative is a Web in which governments or large companies, or frequently a close association of the two, try to control the internet, with packets of information delivered in a way that discriminates for commercial or political reasons. Regimes of every sort spy on their citizens, deriving hugely accurate and detailed profiles of them and their intimate lives. Today, the battle is building. The rights of individual people on the Web are being attacked, and at the moment only a few people really understand and realize what is going on.”

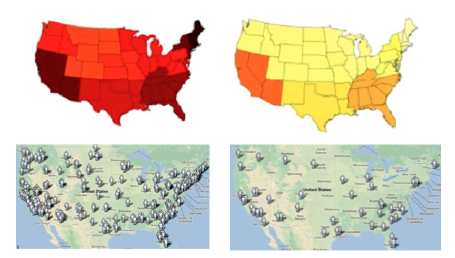 Back in 2008, Google launched its now famous flu trends website. It works on the hypothesis that people make more flu-related search queries when they are suffering from the illness than when they are healthy. So counting the number of flu-related search queries in a given country gives a good indication of how the virus is spreading.
Back in 2008, Google launched its now famous flu trends website. It works on the hypothesis that people make more flu-related search queries when they are suffering from the illness than when they are healthy. So counting the number of flu-related search queries in a given country gives a good indication of how the virus is spreading.